When considering a security system for your business or an upgrade to an existing system,…
A Complete Guide to Biometric Security Measures
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, ensuring the safety and security of sensitive information has become a top priority for commercial businesses. Traditional security measures like passwords and access cards are no longer sufficient to protect valuable assets. This is where biometric security measures come into play.
By utilizing unique physical or behavioral characteristics, biometric security systems provide enhanced protection against unauthorized access and fraud. In this article, we’ll explore the different types of biometric security measures, their various applications, advantages, and considerations for implementing biometric access control in your business.
Continue reading below to learn more and discover how U.S. Protective Services can transform your security experience.
Understanding Biometric Security
Biometric security refers to the use of distinct physiological or behavioral traits to identify individuals and grant them access to restricted areas or sensitive information. These traits include fingerprints, iris patterns, facial features, voice recognition, hand geometry, and behavioral characteristics like gait analysis or keystroke dynamics.
The use of biometrics offers several advantages over traditional security methods. Firstly, it provides a higher level of accuracy in identifying individuals due to their unique biological traits. Unlike passwords or access cards that can be easily shared or stolen, biometrics are inherently personal and cannot be easily replicated.
How Biometric Systems Work
Biometric security systems create a digital representation of specific biological or behavioral characteristics, which is then stored in a database for future comparisons. The process involves two main stages: data collection and analysis.
During the data collection phase, the biometric system scans the individual’s specific trait, whether a facial scan, a fingerprint scan, or a voice recording, among others. The biometric scanner captures the unique patterns and features of the trait, converting the information into a digital format.
The next step is data analysis, where the system processes the scanned biometric information using complex algorithms. These algorithms identify specific data points, known as biometric identifiers, unique to the individual.
For example, in fingerprint analysis, the patterns of ridges and valleys on the finger, the minutiae points, are unique for each individual. Whereas in facial recognition, it might be the distance between the eyes or the shape of the cheekbones.
Once the system has identified these unique identifiers, it creates a biometric template – a mathematical representation of the individual’s unique characteristics. This template is then stored in the system’s database.
When access is attempted, the system scans the individual’s trait again, creating a new biometric template in which the system compares the new template with the one stored in its database.
If the templates match, the system confirms the individual’s identity and grants them access. If they don’t match, access is denied. This process ensures that only authorized individuals gain access, providing a robust level of security.
Types of Biometric Security Systems
As we previously mentioned, there are several types of biometric security systems available today. Let’s explore some of the most common ones:
Fingerprint Recognition
Fingerprint recognition is one of the most widely adopted forms of biometrics in commercial settings. Each person has a unique fingerprint pattern that remains stable throughout their lifetime. Fingerprint scanners capture these patterns by analyzing ridges, furrows, and minutiae points on an individual’s fingertip.
With advancements in biometric technology, fingerprint recognition systems have become more accurate and efficient. They are easy to use, cost-effective to implement at any scale, and highly reliable.
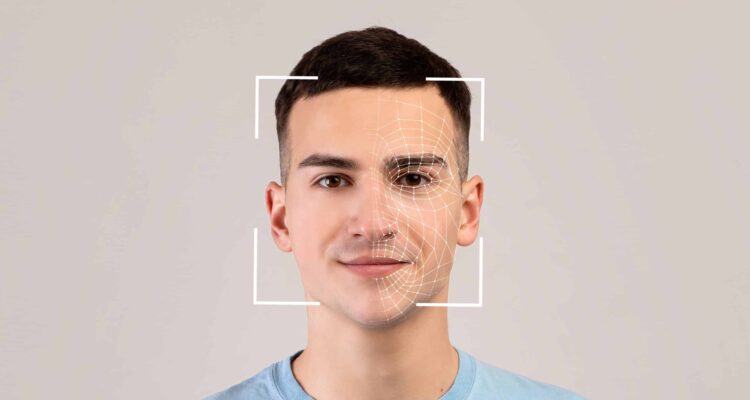
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology analyzes unique facial features to verify a person’s identity. It captures and compares facial patterns, including distances between eyes, nose shape, and jawline. Face recognition systems use cameras to capture images or videos of individuals for identification.
Facial recognition has gained popularity due to its non-intrusive nature and ease of use. It can be implemented in various settings, such as access control systems or surveillance applications. However, it is essential to note that privacy concerns and potential technological biases still need to be addressed.
Iris Recognition
Iris recognition technology utilizes the unique patterns in an individual’s iris – the colored part of the eye surrounding the pupil. These patterns are stable over time and have a high level of distinctiveness.
Iris scan systems use specialized cameras to capture detailed images of the iris. The captured data is then compared against stored templates for biometric identification purposes. Iris recognition provides a high level of accuracy and is less affected by external factors like lighting conditions or glasses.
Voice Recognition
Voice recognition technology analyzes an individual’s vocal characteristics to verify their identity. This biometric modality captures various voice parameters such as pitch, tone, rhythm, and accent.
Voice recognition systems can be used for access control or authentication purposes over phone calls or other communication channels. They provide convenience and are particularly useful in scenarios where hands-free operation is required.
Hand Geometry
Hand geometry biometrics analyze the physical features of an individual’s hand, including finger lengths, widths, palm size, and knuckle position. Hand geometry scanners capture three-dimensional images or measurements using sensors.
Hand geometry systems are often used in environments where hygiene is crucial since they do not require physical contact with the scanning device. They are widely adopted in industries such as healthcare or manufacturing.

Advantages and Considerations for Implementing Biometric Access Control
Implementing biometric access control offers several advantages for commercial businesses:
Enhanced Security: Biometric systems provide a high level of security by relying on unique biological traits, significantly lowering the risk of unauthorized access or identity theft. For instance, fingerprint readers and iris recognition scanners offer precise individual identification that is hard to duplicate or forge.
Convenience: Biometric authentication systems eliminate the need for physical tokens or passwords, making them more user-friendly and efficient.
Audit Trails: Biometric systems can generate detailed logs and audit trails, allowing businesses to track and monitor access attempts for accountability, which is crucial for maintaining accountability and security in high-risk areas.
Scalability: Biometric solutions can be easily scaled up to accommodate a growing workforce or expanding infrastructure, offering a flexible and long-term security solution.
However, there are some considerations businesses should keep in mind before implementing biometric access control:
Investment and Maintenance Costs: While biometric systems offer advanced security, they require an initial investment in hardware and software and ongoing maintenance. Budgeting accurately for these expenses is crucial for a sustainable implementation.
Privacy and Compliance: Collecting and storing biometric data require stringent privacy measures. It’s essential to comply with relevant personal data protection regulations and to establish robust data management practices to safeguard user privacy.
Error Rates: Although biometrics are generally reliable, they are not infallible. Understanding the system’s false acceptance rate (FAR) and false rejection rate (FRR) will help you select the right system for your needs and prepare for contingencies.
User Acceptance and Training: Introducing biometric systems may require a cultural shift within your organization. User acceptance and proper training are critical to ensure a smooth transition to this advanced security method.
Customized Security Solutions with U.S. Protective Services: Tailoring Safety to Your Needs
Biometric security measures offer commercial businesses an advanced level of protection against unauthorized access and fraud. By leveraging unique physiological or behavioral characteristics, these systems provide enhanced accuracy, convenience, and scalability compared to traditional security methods. With proper planning and implementation, biometrics can become a valuable asset in securing your business’s sensitive information and assets.
The safety of your business isn’t just a necessity — it’s a priority. At U.S. Protective Services, we crafted our state-of-the-art security solutions with cutting-edge technology tailored to the unique needs of your business. Our comprehensive monitoring systems are designed to deliver top-tier security effortlessly, ensuring you the peace of mind you deserve.
Don’t wait for a security breach to remind you of what’s at stake. Contact U.S. Protective Services today to learn more about our custom security solutions and step into a more secure tomorrow. Our team of experts is committed to guiding you through every step, ensuring your specific needs are met with the highest standards of protection and professionalism.



